






















Ducks are among the most widely recognized and beloved waterfowl in the world. These feathered creatures are found in various habitats across the globe, from serene ponds and tranquil lakes to bustling urban parks. Ducks are fascinating not only due to their distinctive characteristics but also because they play essential roles in the ecosystems they inhabit.
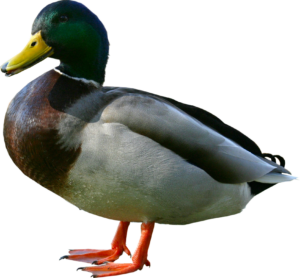
Ducks belong to the family Anatidae, which also includes swans and geese. These birds are characterized by their webbed feet, which make them exceptional swimmers, and their distinctive bills, adapted to their feeding habits. Duckbills vary in shape and size, depending on the species. They are designed for foraging, filtering food, and even straining tiny organisms from the water.
Ducks come in a remarkable array of colors and plumage patterns, making them visually captivating. Their feathers are essential for insulation, buoyancy, and protection from the elements. Male ducks, known as drakes, often sport more vibrant and colorful plumage than the more subtly colored females.
Ducks are highly adaptable birds, and they can be found in a wide range of habitats, from freshwater wetlands and marshes to coastal estuaries and even urban environments. They are known for their distinctive quacking sounds, although vocalizations vary among different duck species. These calls serve various purposes, such as communication between individuals and signaling danger or courtship.
One of the most remarkable aspects of duck behavior is their migratory patterns. Many duck species are migratory, traveling great distances between breeding and wintering grounds. This fantastic journey showcases their navigational abilities and ability to adapt to different environments.
Ducks are omnivorous, meaning they have a varied diet, including plant matter and tiny aquatic organisms. They feed on aquatic plants, algae, small fish, and invertebrates, using their specialized bills to filter or dabble for food. Their ecological role as herbivores helps control plant populations in wetland ecosystems and contributes to nutrient cycling.
Ducks play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the ecosystems they inhabit. By feeding on aquatic plants and invertebrates, they help control the populations of these organisms, preventing overgrowth in marine ecosystems. Moreover, ducks are part of the food chain, providing sustenance for predators such as foxes, raccoons, and various bird species.
Ducks also serve as indicators of ecosystem health. Changes in duck populations can be a warning sign of environmental problems, such as pollution, habitat degradation, or climate change. Conservation efforts to protect ducks and their habitats have far-reaching benefits for biodiversity and overall ecosystem stability.
Ducks have been a part of human culture and folklore for centuries. They are commonly depicted in art, literature, and mythology. People worldwide also enjoy ducks for their beauty and as a food source.
Ducks have been domesticated in many regions for their eggs, meat, and feathers. They have become symbols of prosperity and good luck in some cultures. Duck hunting has been a popular recreational activity in various parts of the world, although it is subject to strict regulations to ensure the sustainability of duck populations.







Leave a Comment