



















The Indian flag, also known as the tricolor or Tiranga, is one of the most recognizable symbols of India’s identity and sovereignty. It represents the aspirations, struggles, and achievements of the Indian people throughout history. The flag is a powerful emblem that embodies the spirit of unity, pride, and diversity that characterizes this vast and culturally rich nation.
The idea of a unified national flag for India was conceived during the struggle for freedom against British colonial rule. In 1921, the Indian National Congress adopted the tricolor design with horizontal stripes of saffron, white, and green, symbolizing the unity of Hindus (saffron), Muslims (green), and other religions (white). The center’s spinning wheel, or “Charkha,” represented self-reliance and the Swadeshi movement. The current design of the Indian flag was adopted on July 22, 1947, shortly before India’s independence, with the addition of the Ashoka Chakra in the center, replacing the Charkha.
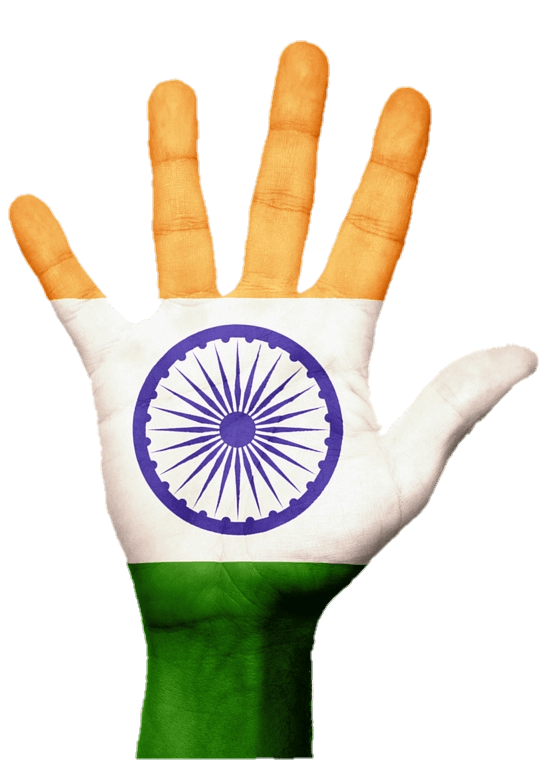
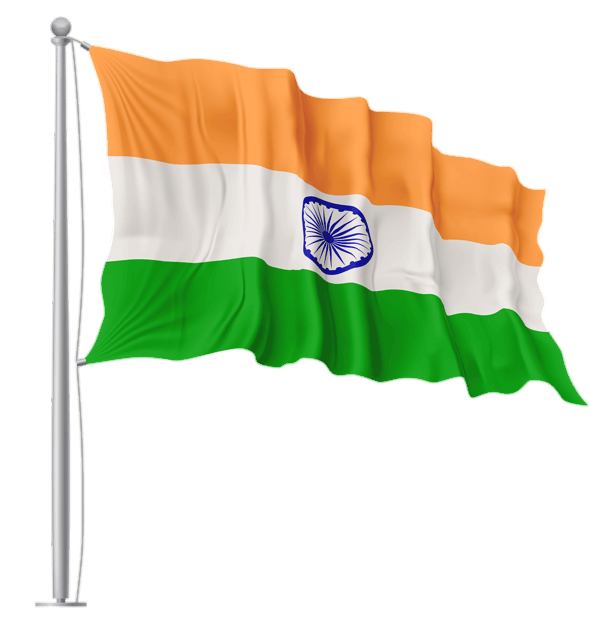
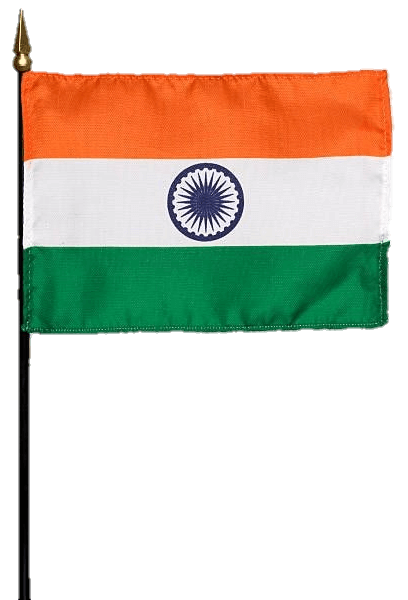
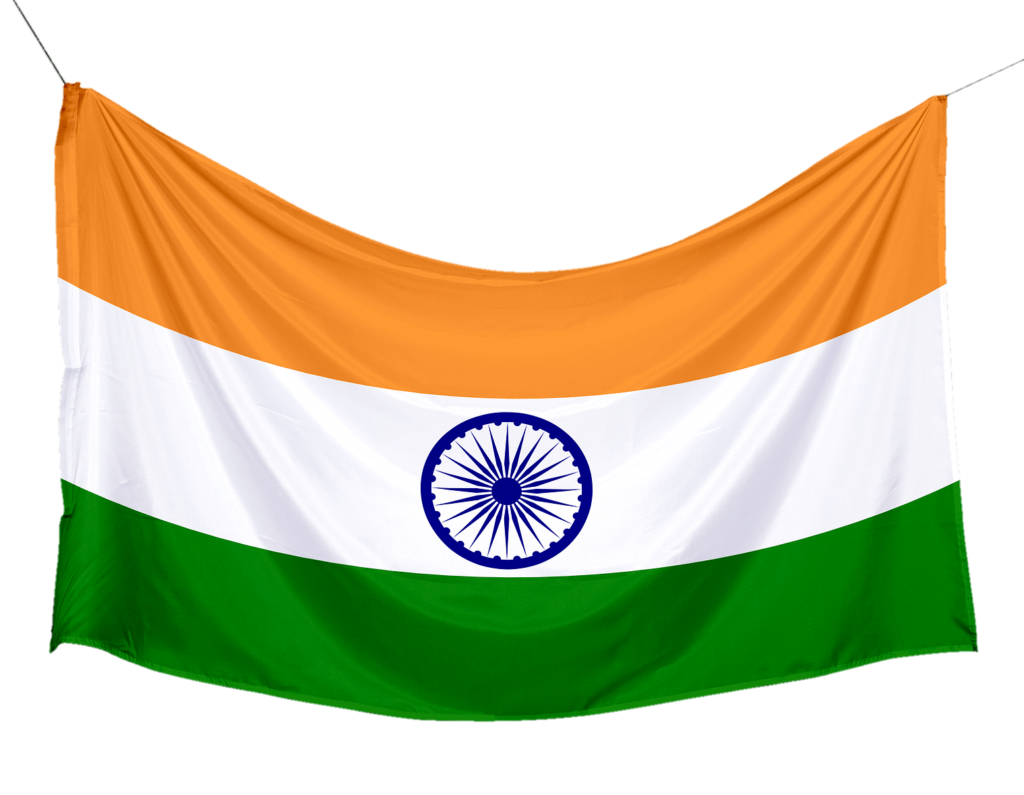
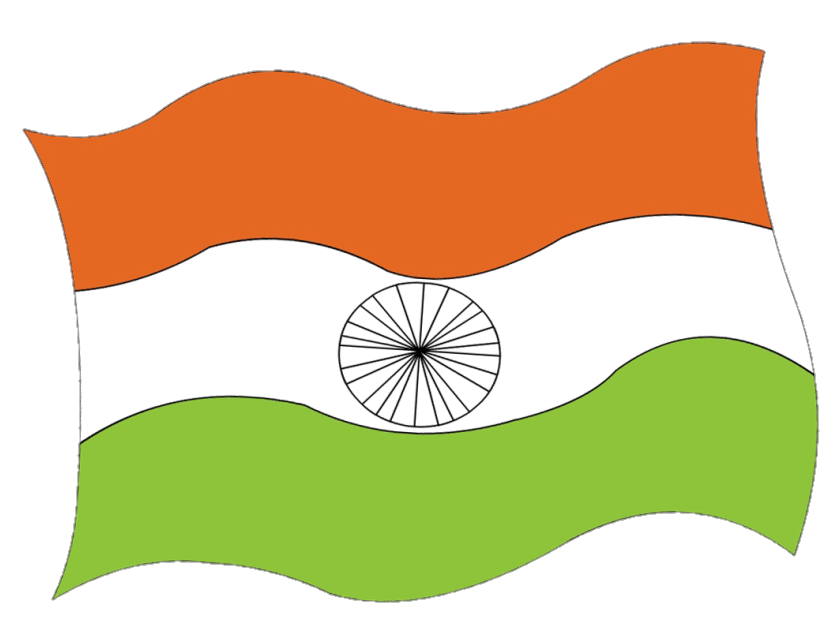
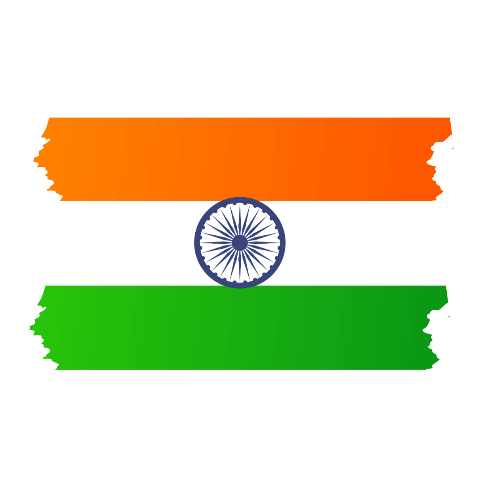
The Indian flag is a horizontal tricolor of equal width with three colors: saffron at the top, white in the middle, and green at the bottom. Each color has its significance. Saffron represents courage, sacrifice, and the spirit of renunciation. White symbolizes peace, purity, and truth, which are the foundations of India’s spiritual and moral values. Green signifies growth, fertility, and auspiciousness, reflecting the nation’s agricultural heritage.
The Ashoka Chakra, a navy blue wheel with 24 spokes, occupies the center of the white stripe. The Chakra is inspired by the Lion Capital of Ashoka, an ancient Indian sculpture, and represents the eternal wheel of law, righteousness, progress, and movement.
The Indian flag embodies several profound meanings that resonate with the nation’s ethos:
Unity in Diversity: India is a diverse land with multiple languages, religions, and cultures. The tricolor represents the harmony and unity that binds this vast nation together, transcending regional, linguistic, and religious boundaries.
Freedom Struggle: The flag symbolizes India’s long and arduous struggle for independence from British rule. It reminds us of the sacrifices made by countless freedom fighters who fought bravely for the nation’s freedom.
National Pride: The flag instills a sense of pride and patriotism among Indians. It is a representation of their shared heritage and the accomplishments of the nation on the global stage.
Secularism: The tricolor’s saffron, white, and green colors signify India’s commitment to secularism, embracing all religions and fostering an atmosphere of religious tolerance.
Sovereignty and Independence: The adoption of the Indian flag marked the transition from a colonized nation to a sovereign and independent republic.
The Indian flag is more than just a piece of cloth; it is a vibrant emblem that embodies the rich tapestry of India’s past, present, and future. It symbolizes unity, pride, diversity, and freedom, inspiring every Indian to stand together as one nation. The flag remains a constant reminder of the sacrifices made to achieve independence and the responsibility to uphold the democratic values that define the Indian nation. As India continues its journey towards progress and prosperity, the Tiranga will forever flutter high, representing the hopes and aspirations of over a billion people.






Leave a Comment