This gallery shows 40+ High Quality and Best Resolution Skull PNG Images, Vectors, Stickers, logos, Icons, and Clipart Pictures with transparent backgrounds. Free download all these Skull Png Images for graphic design, projects, presentations, web design, editing, and other works.
Skull PNG Images:
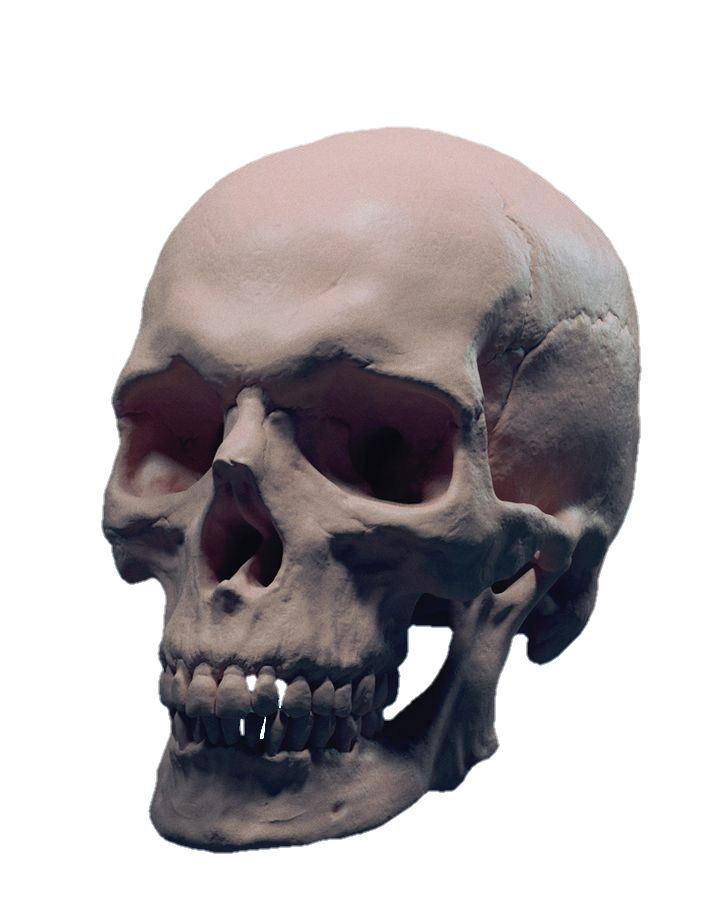
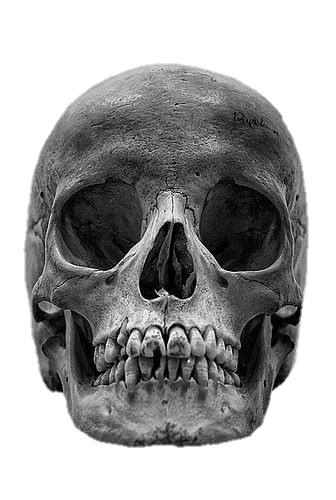












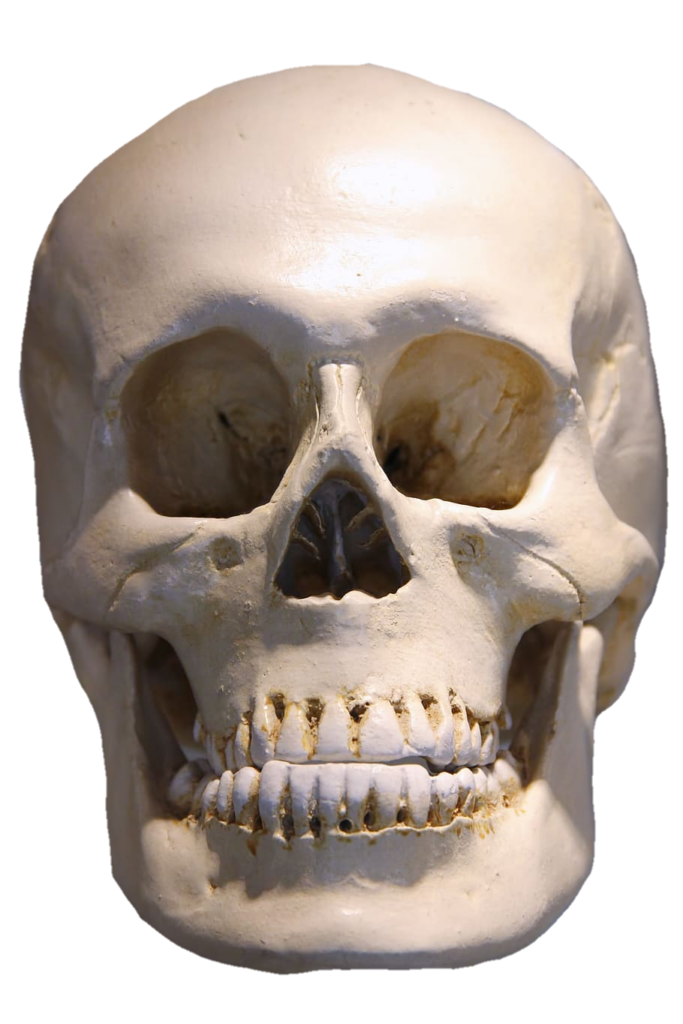

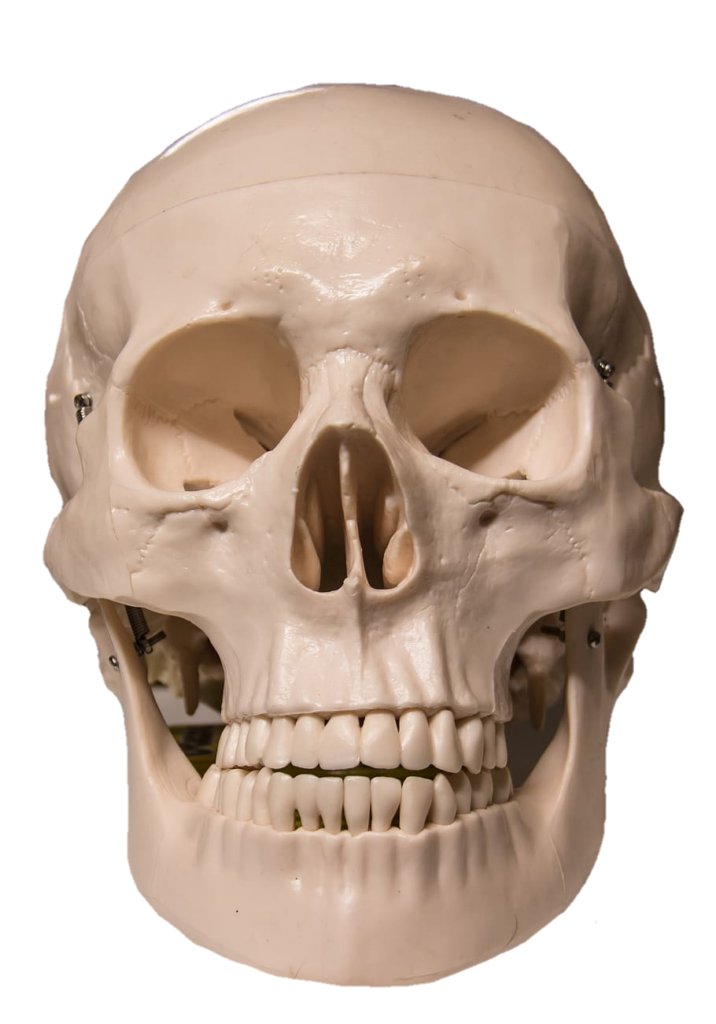










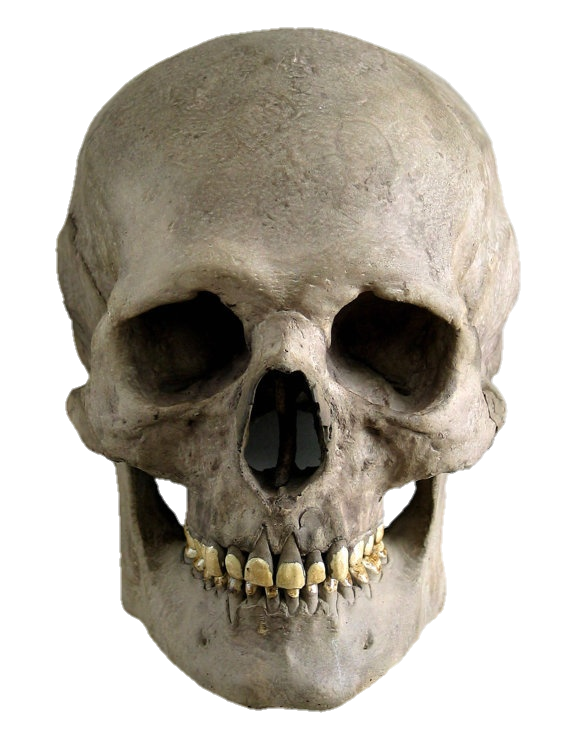
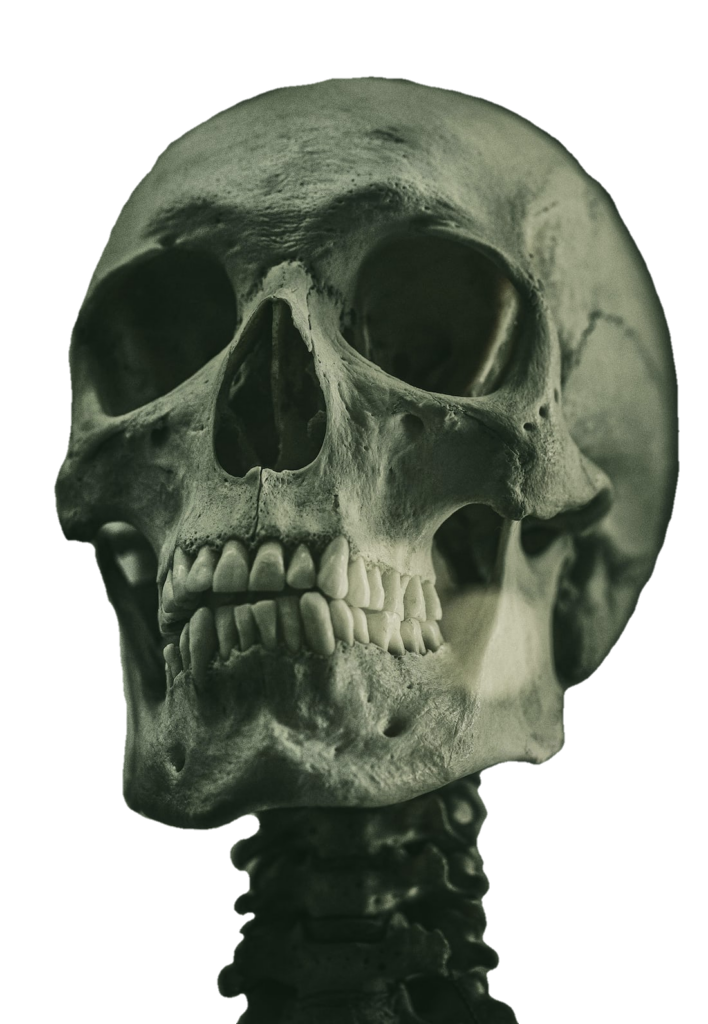


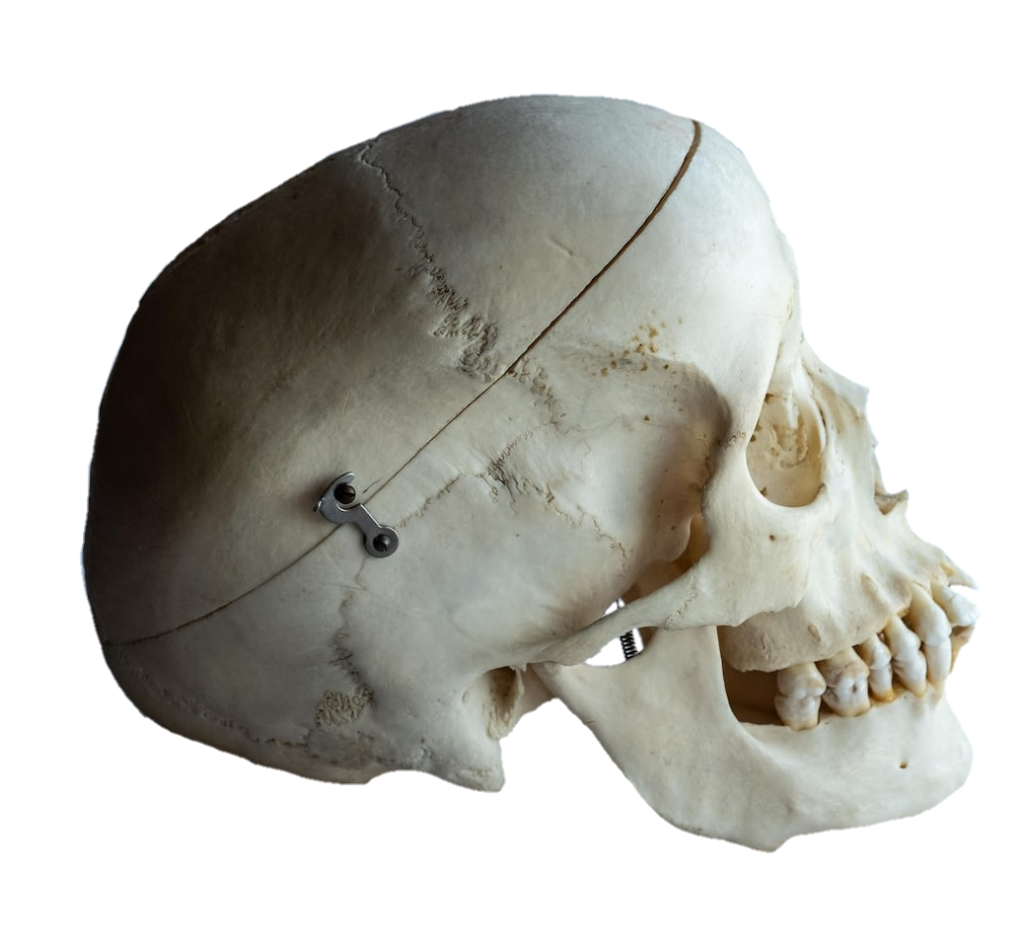
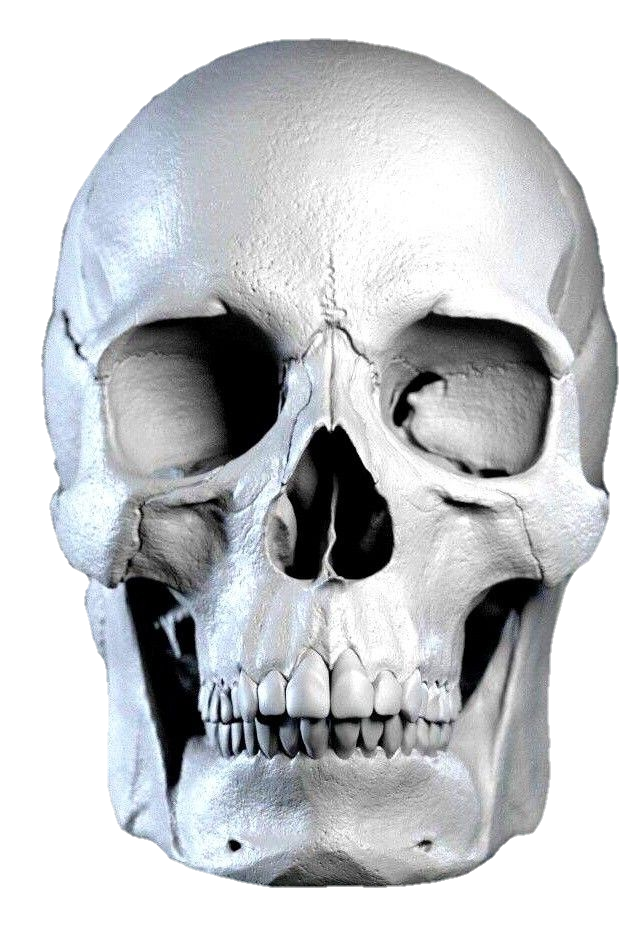
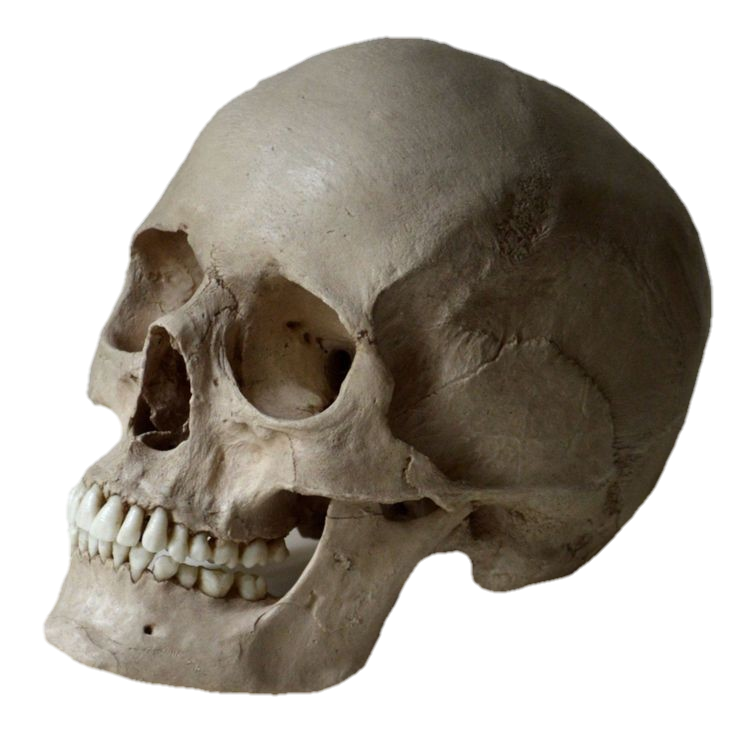

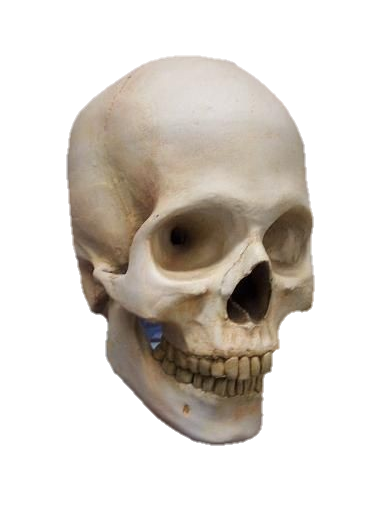

The skull, the bony structure of the head of vertebrates, with bones or cartilages, forms a single layer protecting the brain and some sensory organs. The upper jaw, but not the lower, is part of the skull. The human skull, the part that contains the brain, is round and slightly larger compared to the face. In most other species, the anterior portion of the skull, including the upper teeth and snout, is larger than the skull. In humans, the skull is supported by the highest vertebrae, called the atlas, which allows the head to be tilted. The atlas rotates the next lower vertebra, the axis, to allow side-to-side movement.
Anatomy: The human skull consists of 22 vertebrae, 8 cranial vertebrae, and 14 facial vertebrae. These bones are held together tightly by ligaments, which form a fibrous joint that allows us to move freely during birth and development but fuse as we age. The main bones of the skull are the frontal-parietal (pair of pairs), parietal (pair of pairs), pelvis, sphenoid, and ethmoid. The facial bones include the maxilla (upper jaw bone), mandible (lower jaw bone), palate, zygomatic bone (cheek bone), and others. Anatomy: The human skull consists of 22 bones, 8 cranial bones, and 14 facial bones. These bones are held tightly together by ligaments, which form a fibrous joint that limits our mobility during birth and development but fuses together as we age. The main bones of the skull are the frontal-parietal (pair of pairs), parietal (pair of pairs), pelvis, sphenoid, and ethmoid. The facial bones include the maxilla (upper jaw bone), mandible (lower jaw), jaw bone, zygomatic bone (cheek bone), and others.
Facial Bones: The facial bones form the structure of the face and support important sensory organs such as the eyes, nose, and mouth. These bones also play a role in chewing and articulating speech. The maxilla forms the upper jaw, while the mandible forms the lower jaw and is the only movable bone in the skull.
Paranasal Sinuses: The skull contains four pairs of air-filled paranasal sinuses (frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and maxillary) within certain facial bones. These sinuses help reduce the weight of the skull and enhance resonance in our voice. They are also involved in warming and humidifying the air we breathe.
In precis, the human skull is a problematic structure with numerous capabilities, protecting the brain, supporting sensory organs, and providing important passages for nerves and blood vessels. Its shape and functions have advanced to fulfill the desires of our species and mirror our biological and evolutionary history.






Leave a Comment
Instagram